Echinococuss granulosus (continue)
- To describe hydatid cyst.
-
To know
the pathognomonic symptoms and signs.
-
To
explain why these symptoms and signs occur.
-
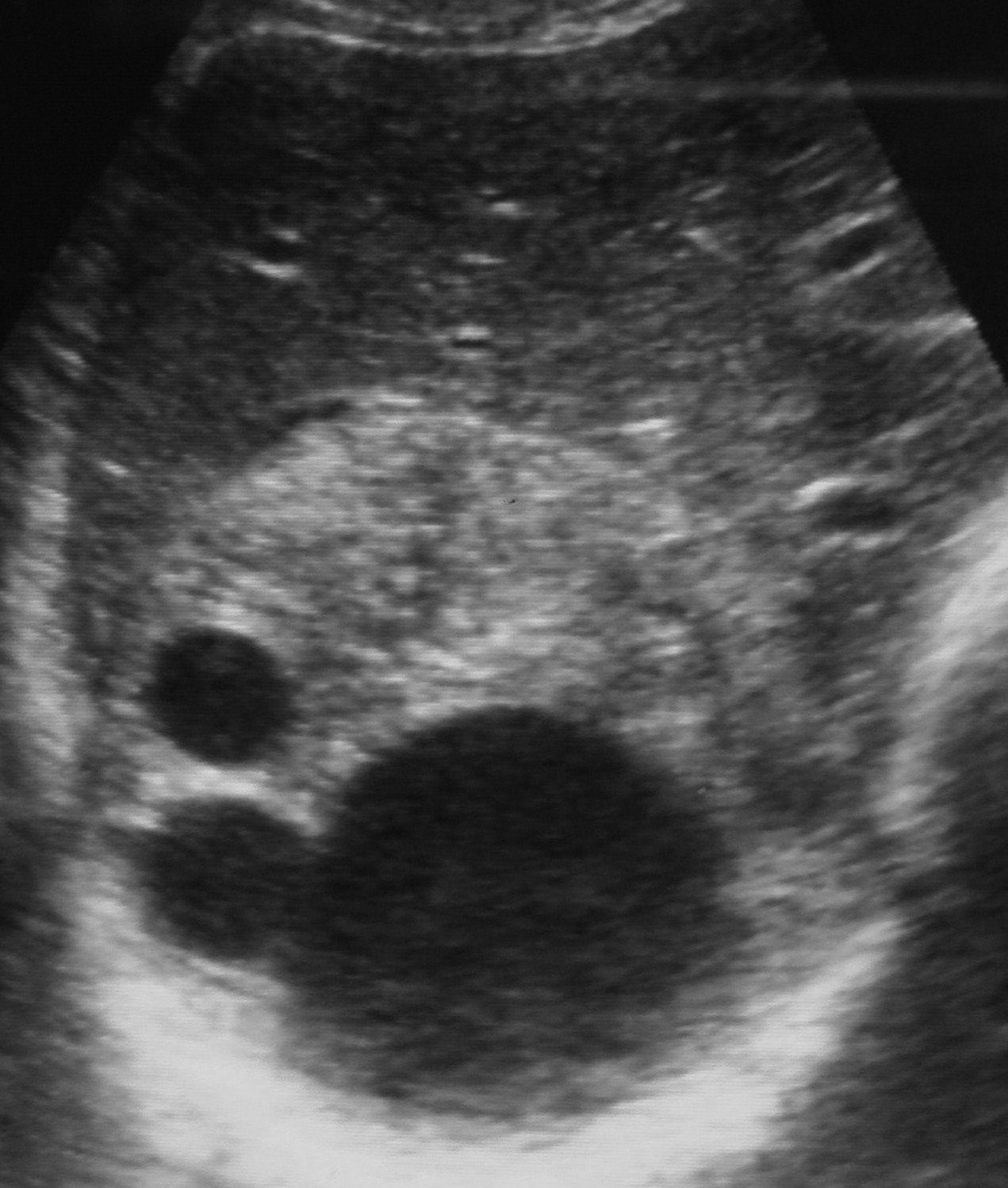
The fully developed cyst is typically
unilocular, spherical and filled with fluid. It reaches a diameter of 10 cm or
more (this takes many years).
-
The cyst wall is differentiated from the
following layers from inside to outside:
1.
Cellular or germinal layer which is
capable of division.
2.
Elastic non cellular laminated layer.
3.
Host produced fibrous tissue layer to
prevent further growth to the cyst.
-
The cyst contains:
1.
Individual scolicies (microscopic, about
100-1000).
2.
Daughter cyst similar to mother cyst.
3.
Brood capsules which are sacs
enclosing a number of scolices.
All
these contents may remain attached to the wall of the mother cyst, or may be
detached and fall in the cavity forming hydatid sand.
-
Exogenous daughter cyst occurs as a result of
herniation of germinal layer to the outside.
- Sometimes,
the germinal layer of the mother, daughter cysts and brood capsules fail to
give scolices forming what is called sterile cyst.
Symptoms are often related to
site of the cyst:
-
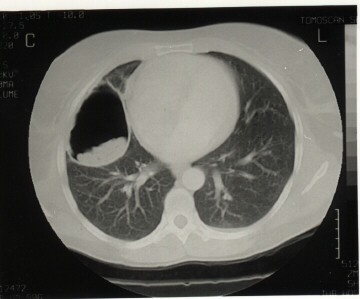
Hepatic cyst (about 66%):
Usually is found in the right lobe towards the inferior surface and extends into the abdominal cavity or in the dome of the liver, grows slowly before producing marked symptoms:
1. Asymptomatic, it will be noted only if it increases in size.
2. Expansion produces pressure on blood vessels or bile duct (producing obstructive jaundice).
3. Rupture of the cyst (due to coughing, muscle strain and operative procedure) leads to one of the following:
· Secondary new cysts, through seeding the peritoneal cavity with hydatid sand or bits of germinal layer.
· Rupture into bile ducts leads to intermittent jaundice, fever and eosinophilia.
· Allergic manifestations up to anaphylactic shock in case of sudden rupture with entrance of a considerable hydatid material in the blood stream.
-
Pulmonary cyst (about 22%):
- Early
symptoms include haemoptysis, transient thoracic pain and shortness of breath.
- In majority of cases, the cyst transfers into chronic
pulmonary abscess (if rupture is incomplete) and the patient complains of
sudden attack of cough with sputum containing frothy blood, mucus and hydatid material.
Jaundice may be one of the manifestations of :
|
Enterobiasis | |
|
Hydatidosis | |
|
H. nana infection | |
|
Heterophyiasis
|