Echinococcus granulosus (continue)
-
To know the pathognomonic symptoms and
signs.
- To
explain why these symptoms and signs occur.
- To know the available tools for proper diagnosis of hydatidosis.
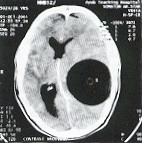
- Brain cyst (about 1%):
Large cyst leads to symptoms of
increased intracranial tension up to epilepsy.
- Renal cyst (about 3%):
It leads to intermittent pain and haematuria. The hydatid sand may be present in urine.
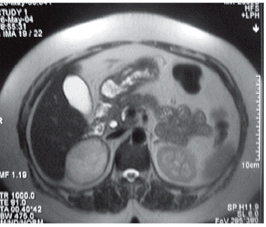
- Osseous cyst (about 2%):
It has no fibrous tissue layer nor laminated layer, but only germinal layer, which develops first in the marrow cavity then extends to the osseous tissue leading to:
1. Erosion of large area of bones.
2. Destruction of the trabeculae.
3. Spontaneous fracture.
- Clinically: By the presence of a slowly growing cystic tumor and history of close contact with dogs.
- Imaging techniques:
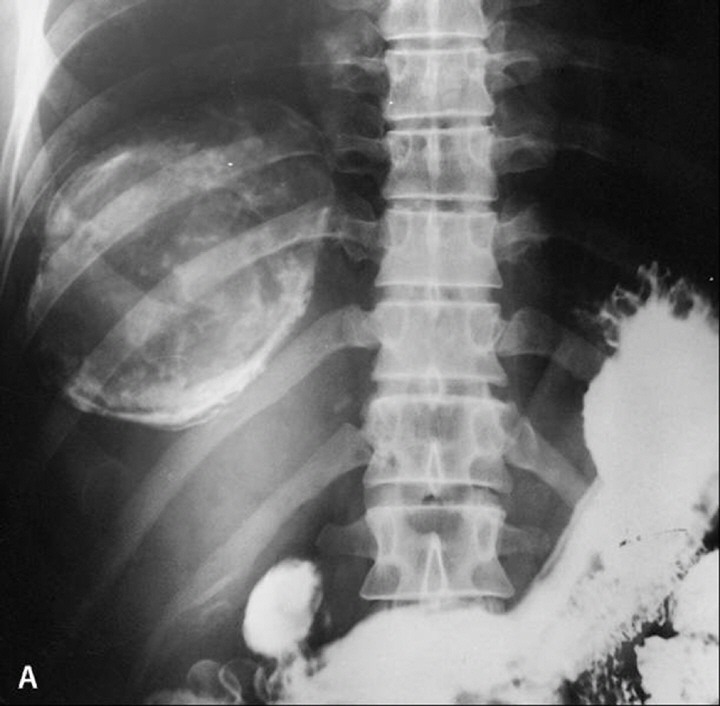
A. X-ray: especially in pulmonary cysts and calcified cysts:
i. Round solitary or multiple sharply contoured cysts of 1-5 cm in diameter.
ii. Internal daughter cysts give a car wheel appearance.
iii. Thin crescent or ring shape calcification.
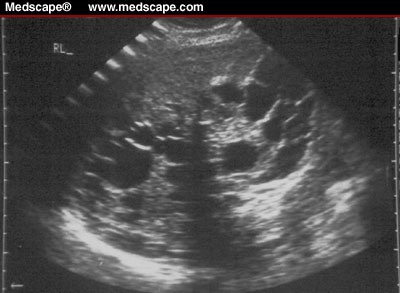
B. Computerized tomography (CT) and Ultrasonography detect uncalcified cysts and of value in the following up of treated cases.
- Laboratory diagnosis:
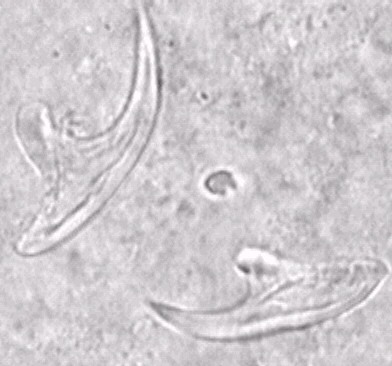
- Aspiration cytology using trichrome staining of the filtered aspirate to show acid fast hooklets. This procedure is risky and may cause transplantation of the germinal layer and formation of new cysts or anaphylactic shock.
- Finding hydatid material after surgical removal of the cyst or finding hydatid fragments from a ruptured cyst in the sputum or urine.
c. Serological tests → IHA or ELISA
↓
→ Immunoelectrophoresis to detect antigen 5 or arc 5
- Molecular diagnosis by DNA analysis and PCR.
- Intradermal test of Casoni was used for a long time in diagnosis but it is not preferred because it may give allergic reactions.
True False