Cysticercosis
Cysticercosis
is the
invasion of human tissues by cysticercus cellulosae, the larval stage of T.
solium (man acts as intermediate host).
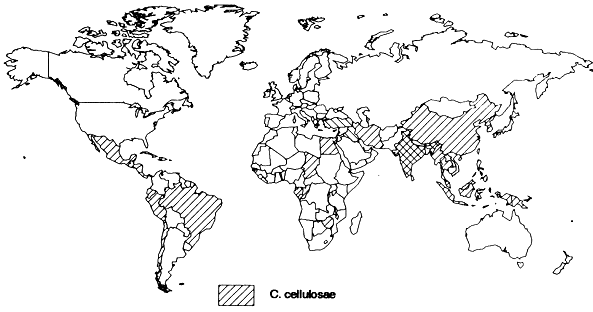
Cosmopolitan especially in pig raising countries.
Ingestion of eggs of T. solium by one of
the following ways:
This is called Heteroinfection
- Contaminated food or drink with eggs
This is called External autoinfection
- Hand to mouth infection in a patient having adult worms in his intestine
This
is called Internal autoinfection
- In
a patient having adult worms in his intestine, some detached segments may
ascend by antiperistaltic movements to the stomach then descend again to the
intestine where they hatch and cause cysticercosis
In the small intestine, onchosphere hatches, penetrates intestinal mucosa to the circulation to various tissues and changes into cysticercus cellulosae.
Man
can act as both final and intermediate host in the following parasitic
infection:
|
Ascaris lumbricoides infection. | |
|
Taenia solium infection. | |
|
Fasciola infection.
| |
|
Schistosoma mansoni infection.
|